Avoiding a Cartography Catastrophe
Study recommends new tools to improve global mapping of infectious disease
February 4, 2013
|
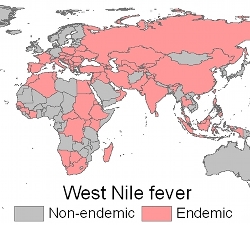
| An online, open-access database included in the study evaluates the quality of data available for all clinically important infectious diseases known to humans, such as West Nile fever. |
Since the mid-nineteenth century, maps have helped elucidate the deadly mysteries of diseases like cholera and yellow fever. Yet today's global mapping of infectious diseases is considerably unreliable and may do little to inform the control of potential outbreaks, according to a new systematic mapping review of all clinically important infectious diseases known to humans.
Of the 355 infectious diseases assessed in the review, 174 showed a strong rationale for mapping and less than 5 percent of those have been mapped reliably. Unreliable mapping makes it difficult to fully understand the geographic scope and threat of disease and therefore make informed policy recommendations for managing it, write the authors of the study, which appears as open access on Feb. 4 in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B.
An online, open-access database, which accompanies the study, provides a quantitative scheme for evaluating the quality of data available for each infectious disease as well as specific mapping recommendations for each disease. Among the recommendations for improving disease cartography are the use of new crowdsourcing techniques to gather data, such as analyzing the content and frequency of Twitter messages about disease. Twitter feeds during the 2009 H1N1 flu outbreak, for example, predicted outbreaks sooner than traditional disease surveillance methods.
"We have shown that novel solutions exist to enable us to use up-to-date data and technology to rapidly improve our geographic knowledge of a wide range of clinically important pathogens," said Katherine Battle, one of the study's co-authors from the University of Oxford.
Unique to the review is the inclusion of how the basic reproduction rate, which is the primary epidemiological number used to determine the degree which a disease can spread through a population, might vary among pathogens.
"There is a clear need for better estimates of the potential growth of infectious diseases that allow spatial variations to be taken into consideration, and this paper is a wonderful contribution to help us meet this need," said Louis Gross, the director of the National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis, which sponsored a workshop in 2011 that produced the paper.
Citation: Hay SI et al. 2012. Global mapping of infectious disease. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. Published [online] 4 February 2013.
Contact Information:
Catherine Crawley, NIMBioS at ccrawley@nimbios.org; 865-974-9350
Katherine Battle, University of Oxford at katherine.battle@zoo.ox.ac.uk; +44 1865 281210
#
The National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis (NIMBioS) brings together researchers from around the world to collaborate across disciplinary boundaries to investigate solutions to basic and applied problems in the life sciences. NIMBioS is supported by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture with additional support from The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
NIMBioS
1122 Volunteer Blvd., Suite 106
University of Tennessee
Knoxville,
TN 37996-3410
PH: (865) 974-9334
FAX: (865) 974-9461
Contact NIMBioS


